前言
从今日起,陆续分享《HeadFirstJava》的读书笔记,希望能够帮助大家更好的理解Java,提高自己的基础编码能力。
Java是一门面向对象的高级编程语言,常年霸占编程语言排行榜前三。
Java是目前国内的主流开发语言,基本每家大型公司都对Java开发工程师有巨大需求,因此打好Java基本功对我们的职业生涯有很好的帮助。
今天要分享的是【类与对象-拜访对象村】,希望对大家有所帮助。

面向对象 vs 面向过程
面向对象会让你的生活(程序设计)更美好
书籍精华
对象村

//阿珠-面向过程的开发者代表
rotate(shapeNum) {
//旋转360°
}
playSound(shapeNum) {
//查询播放哪个AIF文件
//播放
}
//阿花-面向对象的开发者代表
class Square {
rotate() {
//code to route a square
}
playSound() {
//code to play the AIF file for a square
}
}
class Circle {
rotate() {
//code to route a circle
}
playSound() {
//code to play the AIF file for a circle
}
}
class Triangle {
rotate() {
//code to route a triangle
}
playSound() {
//code to play the AIF file for a triangle
}
}

//软件开发最常见的问题就是:需求变更
//针对需求变更,不同开发者有不同的解决方案
//面向过程的开发者代表-阿珠
playSound(shapeNum) {
//如果不是阿米巴原虫
//查询使用哪个AIF文件
//播放
//不然
//播放amoeba.hif
}
//面向对象的开发者代表-阿花【新加入的类不会影响已经测试好的类,适应性和可扩展性好】
class Amoeba {
rotate() {
//旋转
}
playSound() {
//播放
}
}

//好的软件开发上线后,会不断的进行功能的迭代
// 阿珠
rotate(shapeNum,xPt,yPt) {
//如果不是阿米巴
//计算中心点
//然后旋转
//否则
//以xPt和yPt作为旋转中心
//然后旋转
}
// 阿花
class Amoeba {
int xPoint;
int yPoint;
rotate() {
//使用阿米巴的x和y坐标作为旋转中心
//然后旋转
}
playSound() {
//播放
}
}
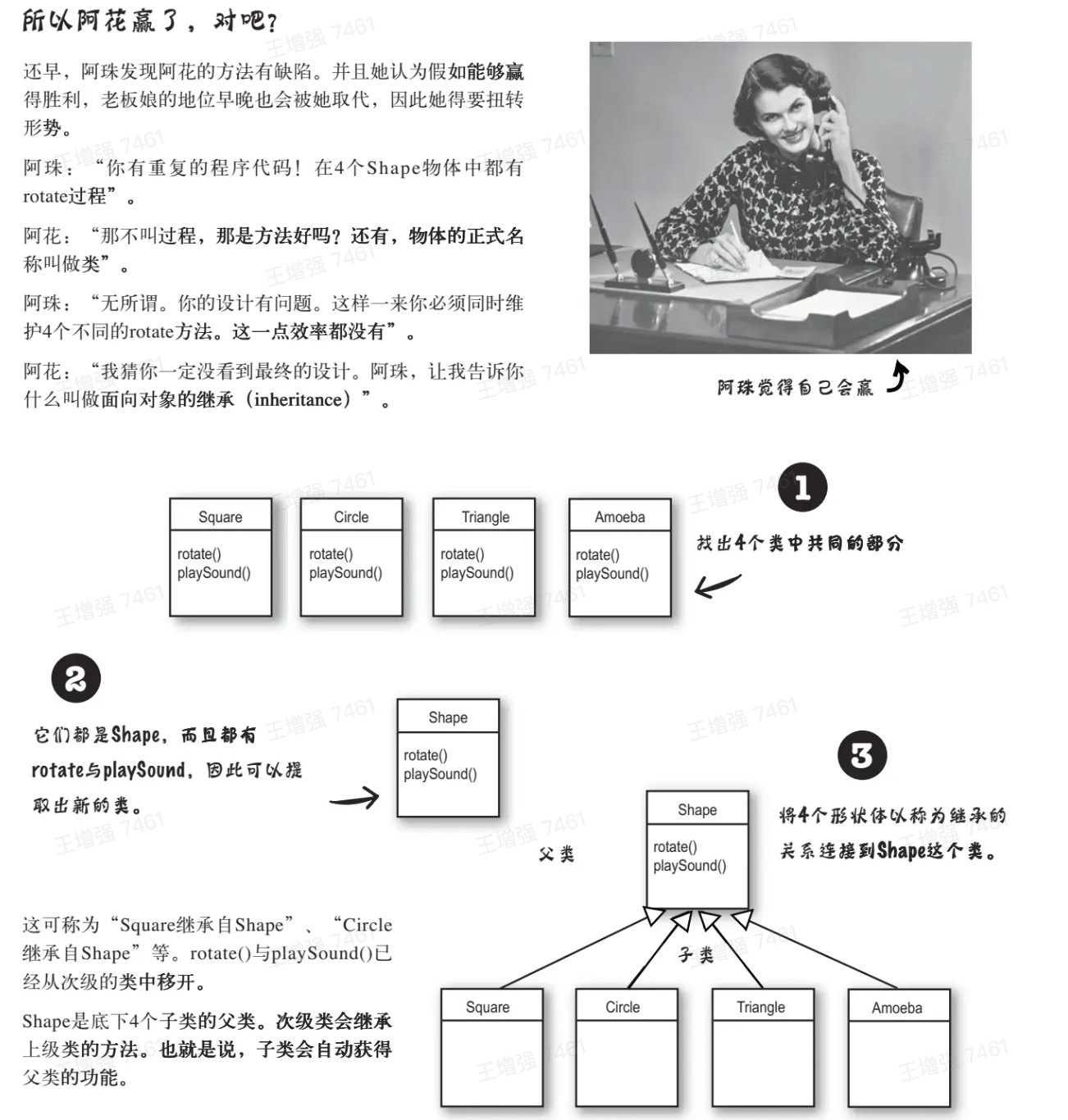
//过程【面向过程叫法】与方法【面向对象叫法】
//面向对象的继承(inheritance)
//阿花的最终设计
class Shape {
rotate() {
//旋转
}
playSound() {
//播放
}
}
class Square extends Shape {
//Square特有的方法
}
class Circle extends Shape {
//Circle特有的方法
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
//Triangle特有的方法
}
class Amoeba extends Shape {
//Amoeba特有的方法
}
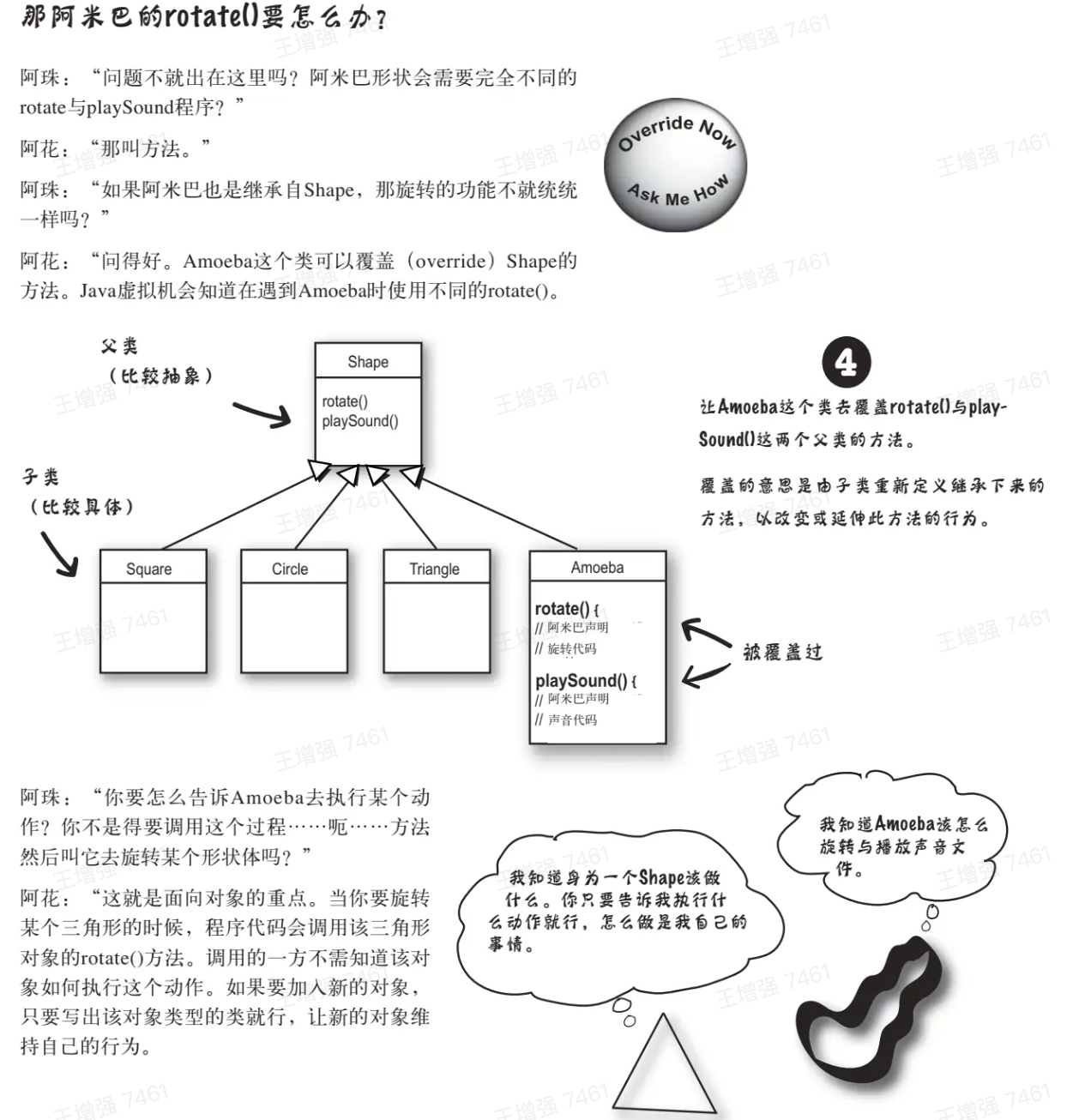
//方法的覆盖(override)
class Amoeba extends Shape {
rotate() {
//阿米巴声明旋转代码
}
playSound() {
//阿米巴声明声音代码
}
}

//面向对象的核心概念:类、对象、方法、属性
以对象来思考

//对象也叫实例,拥有实例变量(instance variable)和方法(methods)
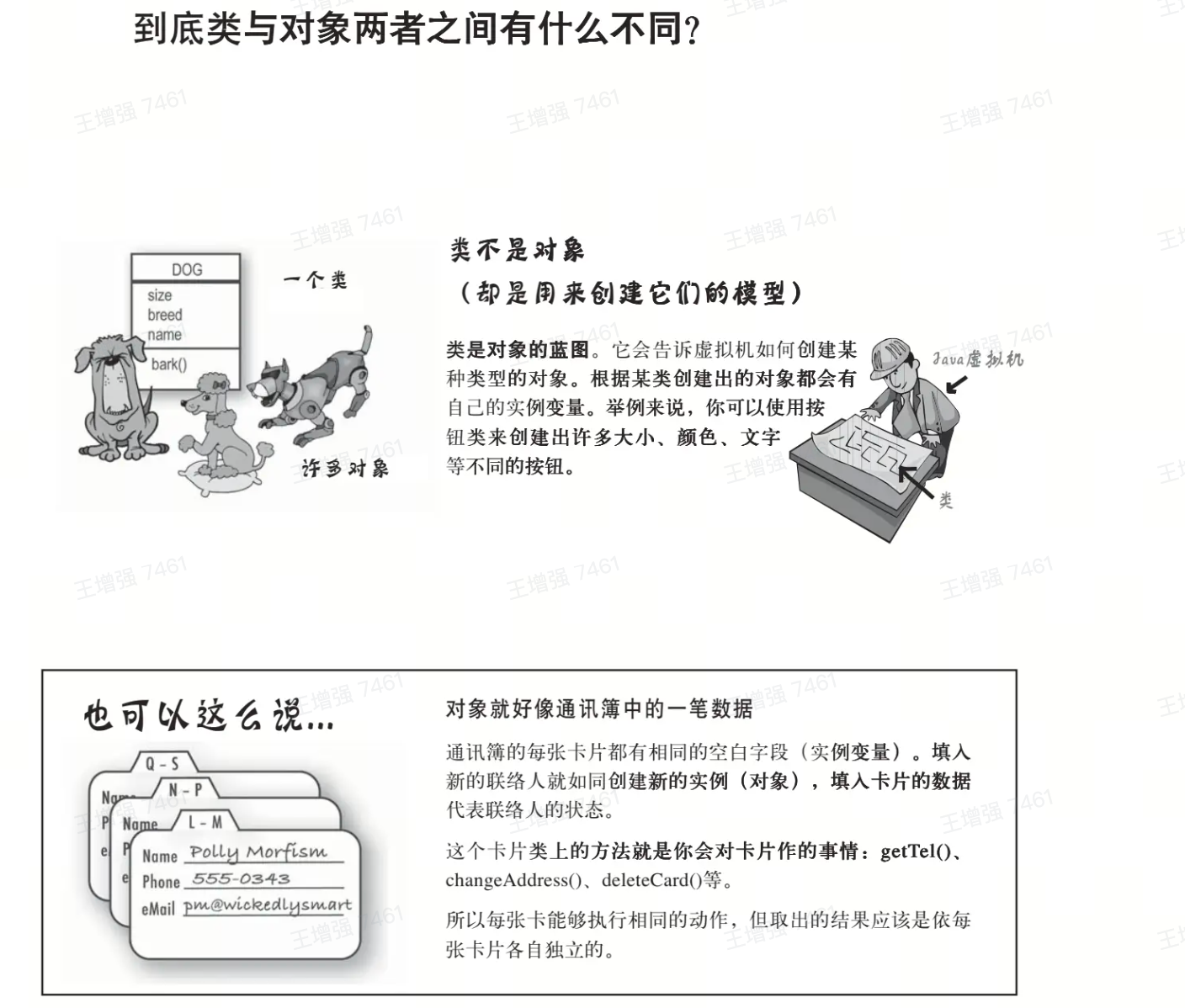
//对象与类,类是抽象的,对象是具体的
//类是对象的蓝图,是创建对象(虚拟机创建)的模型
创建对象

//接下来将经常见到两种类:对象类和测试类(类名TestDrive)
//圆点运算符.用来存取对象的状态和行为
class Dog {
int size;
String breed;
String name;
void bark() {
System.out.println("Ruff! Ruff!");
}
}
class DogTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.size = 40;
d.bark();
}
}

class Movie {
String title;
String genre;
int rating;
void playIt() {
System.out.println("Playing the movie");
}
}
class MovieTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Movie one = new Movie();
one.title = "Gone with the Stock";
one.genre = "Tragic";
one.rating = -2;
Movie two = new Movie();
two.title = "Lost in Cubicle Space";
two.rating = 5;
two.playIt();
Movie three = new Movie();
three.title = "Byte Club";
three.genre = "Tragic but ultimately uplifting";
three.rating = 127;
}
}
逃出main()

//main方法的用途:测试真正的类、启动你的Java应用程序(SpringBoot就是这样做的)

class Player {
int number = 0;
public void guess() {
number = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println("I'm guessing " + number);
}
}
class GuessGame {
Player p1;
Player p2;
Player p3;
public void startGame() {
p1 = new Player();
p2 = new Player();
p3 = new Player();
int guessp1 = 0;
int guessp2 = 0;
int guessp3 = 0;
boolean p1isRight = false;
boolean p2isRight = false;
boolean p3isRight = false;
int targetNumber = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println("I'm thinking of a number between 0 and 9...");
while (true) {
System.out.println("Number to guess is " + targetNumber);
p1.guess();
p2.guess();
p3.guess();
guessp1 = p1.number;
System.out.println("Player one guessed " + guessp1);
guessp2 = p2.number;
System.out.println("Player two guessed " + guessp2);
guessp3 = p3.number;
System.out.println("Player three guessed " + guessp3);
if (guessp1 == targetNumber) {
p1isRight = true;
}
if (guessp2 == targetNumber) {
p2isRight = true;
}
if (guessp3 == targetNumber) {
p3isRight = true;
}
if (p1isRight || p2isRight || p3isRight) {
System.out.println("We have a winner!");
System.out.println("Player one got it right? " + p1isRight);
System.out.println("Player two got it right? " + p2isRight);
System.out.println("Player three got it right? " + p3isRight);
System.out.println("Game is over.");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("Player will have to try again.");
}
}
}
}
class GameLauncher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GuessGame game = new GuessGame();
game.startGame();
}
}
猜数字

//对象存在于【堆内存】中,这里的堆是:可回收垃圾的堆(Garbage-Collectible Heap)
//Java虚拟机会主动帮你管理内存:通过垃圾收集器
你问我答

书籍在线地址
代码在线地址
知识点总结
- 1.面向过程 vs 面向对象
- 2.类与对象
- 3.方法的覆盖
- 4.类的继承
- 5.对象在内存中的存储区域
- 6.垃圾收集器
收获
1.mac如何输入°:
shift+option+8
2.编写伪代码能力
